Prediabetes Is Reversible: Take Action Now
August 3, 2021
Warning Signs Of Diabetes In Children That Every Parent Should Know
August 3, 2021Glycemia is defined as the presence of glucose in your blood. Hypo is derived from the Greek word hupo, which means under or less. Similarly, hyper is derived from the Greek word huper, which means over or above. Thus, hypoglycemia means low blood sugar levels and hyperglycemia means high blood sugar levels. Both these conditions may sound similar, but they have totally different consequences. There may be some overlap between the symptoms of hypoglycemia and the symptoms of hyperglycemia; however, both these conditions are markedly different and poles apart. Let’s explore them further.
Hypoglycemia
When the glucose levels in your blood drop, your body cannot function in a normal manner, and it experiences a wide range of symptoms. The signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia may be mild or extremely intense and even life-threatening.
No two individuals’ bodies are the same. Hence, normal blood glucose levels may vary from person to person. That said, if your blood glucose level is lower than 70 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter), then you have hypoglycemia.
Some individuals may not exhibit any symptoms whereas others may exhibit symptoms that are so severe that immediate medical attention is needed. Symptoms of hypoglycemia may appear immediately after a drop in blood glucose below the normal range. Hypoglycemia can be extremely dangerous because its associated symptoms can leave you unconscious or unable to get any medical help.
Hyperglycemia
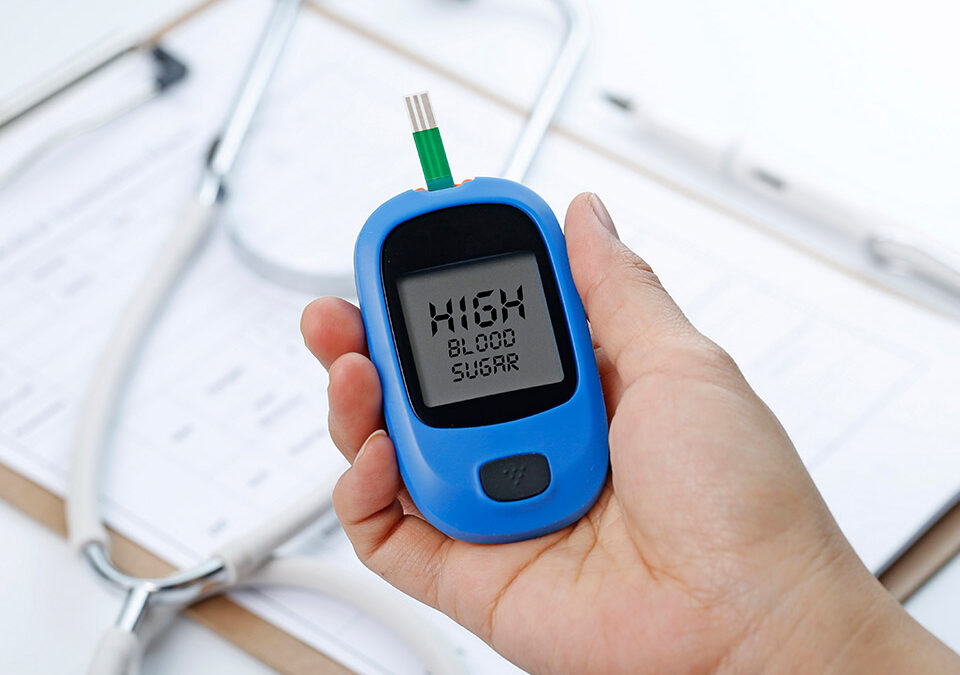
When your blood glucose level is higher than the normal range or greater than 126 mg/dL on two distinct and separate tests, your body experiences hyperglycemia.
If you experience the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia, it eventually means that the insulin produced in your body cannot remove enough sugar from your blood to maintain a normal range. This could be because of two reasons: (1) your body is not producing sufficient insulin or (2) the insulin produced is not working efficiently due to insulin resistance.
Staying in a hyperglycemic state for extended periods of time can be extremely damaging to your body. Health problems such as eye and kidney disease, heart attacks, and even strokes could occur if your blood glucose level is too high for too long.
Hypoglycemia v/s Hypoglycemia (Comparing And Contrasting)
Both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia can affect individuals who have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes. They can additionally affect individuals who are not diabetic, too. Both are concerned with the glucose levels in your body, but they have certain contrasting features.
Whereas hypoglycemia can cause seizures, confusion, coma, or even death, hyperglycemia can lead to nerve damage, circulation disorders, heart attacks, and strokes.
The health concerns are quite different when comparing hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. The common dangers are that if the blood glucose levels remain too low or too high for too long, your body begins to bear the brunt, and you may no longer be able to call for immediate medical help.
Symptoms Of Hypoglycemia v/s Hyperglycemia
Your blood glucose levels can change quickly due to certain medications, levels of activity, and diet. Symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia can manifest immediately after the glucose level in your blood reaches extreme ranges.
Symptoms of both these conditions range from mild to severe, with some individuals not experiencing any symptoms at all. However, most people do experience some symptoms.
Diabetes symptoms of hypoglycemia include:
- Excessive sweating
- Shakiness
- Extreme hunger
- Feeling weak or dizzy
- Irritability
- Headache
- Blurry vision
- Confusion
- Slurred Speech
- Fainting
- Fast or Irregular Heartbeat
- Seizures
- Coma
Symptoms of hyperglycemia in diabetes include:
- Dry mouth (Xerostomia)
- Increased Urination (Polyuria)
- Increased Thirst (Polydipsia)
- Excessive Hunger (Polyphagia)
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Anxiety
- Fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Recurring Infections
- Slow healing of cuts, wounds, and sores
Why Do These Symptoms Matter?
Symptoms of hypoglycemia vs hyperglycemia are essential for diabetics to know because they may encounter low or high blood glucose levels with the passage of time. A virus or cold can cause a spike in blood glucose levels; hence, understanding the symptoms will ensure that diabetics know how to deal with hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Diabetics who can successfully recognise the symptoms can avoid dangerous blood sugar levels that can lead to medical emergencies, including diabetic ketoacidosis.
The Final Word:
Once you understand the symptoms of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, you are in a better position to test quickly and avoid severe problems.
Reference Links:
- https://www.goodrx.com/blog/hyperglycemia-vs-hypoglycemia-whats-the-difference/
- https://flo.health/menstrual-cycle/health/symptoms-and-diseases/hypoglycemia-vs-hyperglycemia
- https://www.diabetes.co.uk/high-low-blood-sugar-symptoms.html
- https://www.woundcareinc.com/resources/hyperglycemia-vs-hypoglycemia-what-you-need-to-know
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/hypoglycemia-vs-hyperglycemia-5179943




