Factors That Can Affect the Accuracy of PPS Test Results and How to Avoid Them
October 15, 2022
Meal Timings and PPS Management
October 20, 2022Hyperglycemia or high blood sugar levels is associated with several diabetes-related complications like heart diseases, strokes, etc. The key to preventing these complications lies in the restoration of glycemic control.
There are several markers for evaluating glycemic control, such as fasting glucose, A1C haemoglobin and postprandial blood sugar. Postprandial blood glucose, or PPS, is nowadays gaining more recognition as it is considered better at predicting diabetes complications, especially cardiovascular diseases.
Many studies have suggested that reducing postprandial blood sugar not only improves glycemic control but also lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases in people with type 2 diabetes. One of the best ways to regulate postprandial blood glucose is physical exercise.
Let’s understand the connection between physical exercises and PPS more in detail here.
How Does Exercise Affect Postprandial Blood Sugar Levels?
Exercise is considered one of the main tools to manage diabetes. When you move your muscles, the cells in your body absorb sugar from the blood to produce energy. Exercising can therefore help lower blood sugar levels for many hours after you stop moving.
The effect of physical exercise on postprandial blood glucose levels is also highly significant. It can help lower postprandial hyperglycemia by increasing contraction-mediated glucose uptake.
When and What Type of Exercises Are Ideal for PPS Management?
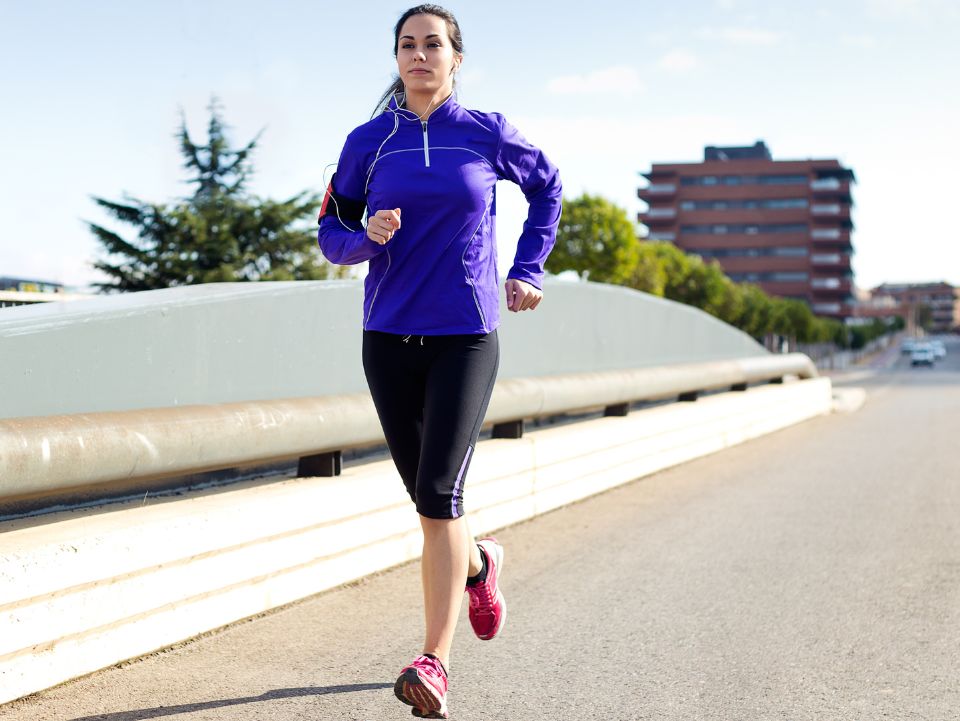

The target blood glucose levels for diabetes patients after 1-2 hours of taking a meal should be 160 mg/dl. For this, postprandial exercise is considered the most beneficial. It is recommended to exercise after 30 minutes of eating for at least 20-40 minutes.
As far as the type of exercise is concerned, any type of physical activity, including brisk walking, is effective in managing postprandial blood sugar levels.
Studies have suggested that aerobic and resistance exercises are most beneficial in improving postprandial glycemia and long-term glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes.
In Summary
Physical exercises play a crucial role in managing postprandial blood sugar levels in the body. It provides not only long-term glycemic control but also a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. The ideal time to exercise is after 30 minutes of eating. You can practise both aerobic and resistance exercises or even take a brisk walk to manage diabetes.
References
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/5/1440/pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5610683/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29396781/
- https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/10.1139/apnm-2021-0168




