Diabetes Numbers: Know Them To Keep Your Diabetes At Bay
June 2, 2021
Does Diabetes Pave Way For Other Chronic Diseases?
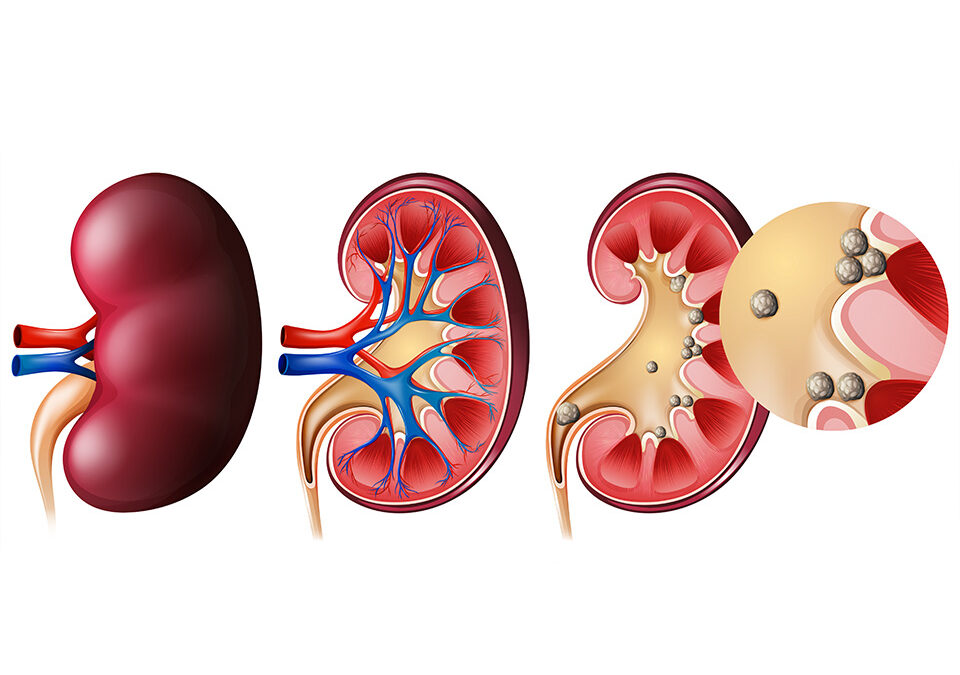
June 2, 2021Diabetes is a health condition that can cause severe health issues when not managed well. One of the many complications that are caused by diabetes is kidney stones. Kidney stones are hard deposits of various minerals and acid salts that crystalize together in concentrated urine that cause excruciating pain when passed. We’ll discuss in-depth the connection between the two conditions and more, and how you can prevent kidney stones by maintaining a healthy diet.
Diabetes And Kidney Stones
In the process of digestion, the body creates waste products. Kidneys have millions of tiny blood vessels known as capillaries which are responsible for squeezing out these waste product from the blood and let useful substances such as protein and red blood cells pass. Diabetic patients have high levels of blood sugar that make the kidneys filter too much blood which gives too much stress on kidneys and thus damage them. Such damage can restrict the kidney to filter certain minerals out of the body, leading to their deposition, which in turn can lead to the formation of kidney stones.
Kidney stones are common among both type 1 and type 2 diabetics and can lead to further complications if not treated timely.
Diabetes and Kidney Stones Symptoms
In the early stage, the symptoms are harder to notice, but they become more evident with time. It is advised to keep a check on symptoms for effective treatment. Some of the common symptoms of kidney stones in diabetes include:
- Protein in the urine
- Reduced need for insulin or diabetes medicine
- Swelling of feet, ankles, hands or eyes
- Increased need to urinate
- Confusion or difficulty in concentrating
- Shortness of breath
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Persistent itching
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills
- Severe pain on either side of your lower back
- Stomach ache that doesn’t go away
Types Of Kidney Stone And Diet Based On Them
Calcium Oxalate Stones:
It is the most common type of kidney stone, and it is created when calcium combines with oxalate in the urine.
Individuals diagnosed with calcium oxalate stones are advised to limit or avoid oxalate food items like nuts and nut product, legumes, rhubarb, spinach, and wheat bran. It may seem that calcium may worsen the situation, but in the right amounts, calcium can block other substances in the digestive tract that may cause stones. It may be best to get calcium from low-oxalate, plant-based foods such as calcium-fortified juices, cereals, bread, some vegetables, and some beans.
Uric Acid Stones:
The natural chemical compound purine found in foods such as organ meats and shellfish leads to a higher production of monosodium urate, which, under some circumstances, may form stones in the kidneys.
Patients with uric acid stones should limit animal protein as it may increase the chances of developing kidney stones. Food items like beef, chicken, pork, eggs, fish and shellfish, milk, cheese, and other dairy products are advised to be avoided.
Although limiting animal protein does not suggest limiting protein itself, patients are asked to consume plant-based protein, sources like legumes, beans, dried peas, lentils, and peanuts; soy foods such as soy milk, soy nut butter, and tofu; nuts and nut products, such as almonds and almond butter, cashews and cashew butter, walnuts, pistachios, sunflower seeds, and other seeds.
Calcium Phosphate Stones:
Calcium phosphate is a minor component of up to 30% of calcium oxalate stones. In this case, it grows until it ruptures through the papillary urothelium and becomes exposed to urine; calcium oxalate crystals nucleate and grow into kidney stones.
Individuals with calcium phosphate stones are advised to limit sodium and avoid the mineral phosphate is primary as the affected kidney is unable to remove extra phosphorus from the blood which weakens bones and damages the blood vessels, eyes, and heart. Food items like meat, dairy, beans, nuts, whole-grain bread, and dark-coloured sodas are high in phosphorus and should be avoided.
Cystine Stones:
These stones are caused due to genetic factors and are descended from generation to generation.
In cystine stones, one should limit sodium as the chances of kidney stones increases by consuming excessive sodium. Drinking plenty of water can also help prevent cystine stones.
Reference Links:
- https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/kidneystones
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/eat-well/what-to-eat.html
- https://www.kidneyfund.org/prevention/are-you-at-risk/diabetes.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-nephropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20354556
- https://www.kidneycareuk.org/about-kidney-health/conditions/diabetes/
- https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/complications/kidney-disease-nephropathy
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/kidney-stones/eating-diet-nutrition